At birth, the eyes of the child are formed and ready to examine the world around. But there is one feature of the structure eyeball in a newborn, regarding the correspondence between the size of the eye and the strength of its optical apparatus. If ultrasound is measured in the size of an eye in a newborn child, then its diameter is about 16.2 mm (in an adult, the size of the eye is 24 mm). This is understandable, because the eye, like any other organ of the child, will have to grow.
At the same time, in the first year of life, the refractive power of the optical apparatus of the eye (refraction) does not correspond to the size of the eyeball. In normal development, it is relatively weak, and this is called farsightednessi.e. refraction «+» .
With farsightedness the image does not focus directly on the retina, but the focus itself is as if behind the eye. Such a relationship between the size of the eyeball and the optical system created by nature is not just. This “stock” of farsightedness, usually 2-4 diopters, is gradually consumed as the child’s eye grows. Usually by 7-10 years old, the eyeball reaches its full size. At the same time, the focus of the image moves directly to the retina and, thus, complete correspondence is achieved between the size of the eye and its refractive power of the optical apparatus. This condition is called emmetropia, that is, zero refraction - no «+» and not «-» .
If, for some reason, the size of the eye continues to increase, then the focus of the image will be in front of the retina and the strength of the optical apparatus becomes stronger than necessary. This state is called myopiaor myopia. Refraction has a sign «-» . This means that the image of distant objects is vague, and the image of loved ones is clear. Thus, it turns out that a short-sighted person sees poorly into the distance and well near.
There are several types of myopia.
The first is associated with various hereditaryor congenital disorders. In this condition, myopia is inherently a disease and can lead to serious consequences. Congenital myopiausually detected in the first year of life and requires a long dispensary observation by an ophthalmologist.
Hereditary myopiamay occur at an older age, has a progressive nature and also requires regular follow-up observation by an ophthalmologist. But there is another type of myopia, which is less associated with the pathological condition of the eye and is not a disease in its essence.
What is the reason?
Today, almost every third inhabitant of our planet has myopia. Nearly 30% of students in developed countries (including Russia) do not see well in the distance and well near, that is, they have short-sightedness. And this is due to our modern lifestyle. Unregulated visual loads, non-compliance with occupational hygiene, as well as excessive enthusiasm for watching TV and computer games, increasing with each passing year, all this leads to an overload of special muscles inside the eye and to their spasm.
At the same time, the first signs of myopia appear:
Gradually, vision begins to deteriorate into the distance;
When viewing distant objects, the child often “squints”;
There may be complaints of discomfort, rapid fatigue, pain in the eyes, itching and even a headache.
All these are signs of developing “false” myopia or so-called accommodation spasm. This condition is reversible, as it is not connected with the size of the eyeball. If you take action in time, you can avoid the appearance of already true myopia, in which the size of the eye exceeds the norm.
What to do to avoid the occurrence of myopia?
First of all, you need a general strengthening of the body, physical activity and a balanced diet. Simply put, a child should not sit for hours at a desk or behind a TV screen and computer, but lead a healthy lifestyle.
Secondly, the observance of the requirements of eye hygiene and, if possible, the limitation of visual work at close range.
These requirements are very simple and come down to a properly organized workplace and correct posture during visual work. Everyone knows that the desktop should be well lit. The light from the table lamp should fall to the left (if the child is right handed). The height of the table and chair should be optimally matched. But this is not the main thing. The main thing - the correct posture and posture of the child at the desk. Very often children take a “recumbent” position at the table. In this case, the load on the visual apparatus increases significantly and contributes to the appearance of "false" myopia. Teach the child to the correct posture: the back is straight, the distance from the table surface to the eye is 30-40 cm. The child should not “lean” on the table with his whole body, but sit so as not to touch even its edge. Do not allow a child to read lying down or in any other position.
Now a few words about the time of visual work.
Many parents are tormented by the question: “How much can a child watch TV or play computer games?” There are no clear norms. One can only say for sure that both in watching TV and playing a computer it is necessary to take breaks - every 30-40 minutes for 10-15 minutes. Especially it concerns the game on the computer. When reading or writing, you should follow the rules set by the school: the duration of the lesson is 40-45 minutes, the duration of the change is 10-15 minutes.
If the child has myopia
Slight myopia (2-3 diopters) is not a tragedy. Given the modern increased visual loads - this is the adaptation of the body to such loads. A myopic eye is much easier to work close to than any other. The main thing in this situation is to stop or slow the progression of myopia and prevent the development of complications.
Preventing the progression of myopia includes a number of different workouts designed to strengthen the intraocular muscle. They are conducted under the guidance of a doctor. But the most important exercise was invented many years ago - “a label on glass”.
Exercise "label on glass"
The child stands in front of the window glass and holds in front of him at a distance of 30-40 see any object (pen, pencil, even just your finger). Initially, the view is directed through the window glass to any object in the distance, better still (car, house, tree, sign).
The selected object is fixed for a few seconds, and then the glance is sharply transferred to a close object in the child’s hand. This close object is also fixed with a glance for a few seconds, and then the visual fixation is transferred back to the distant object. Thus, the child focuses his gaze on a distant, then on a close subject. This exercise is recommended to perform 7-10 minutes several times a day.
In addition to the methods listed above, drug elimination of intraocular muscle spasm arising in response to increased visual loads is widely used. This is achieved by instilling special drops into the eye. Prescribes such treatment only a doctor. He writes a prescription for drops, determines the time of instillation and oversees the treatment process. Do not use drops on your own.
Quite often, various functional disorders in a child’s body can indirectly affect the progression of myopia. This mainly concerns circulatory disorders in the cervical spine, which can be associated with incorrect posture, spasm of blood vessels, as well as with the psycho-emotional state of the child. To identify these related disorders it is recommended to undergo: a Doppler examination of the vessels of the cervical spine, an x-ray of the same section, a consultation with a neuropathologist. Depending on the data obtained, additional therapeutic procedures are prescribed: physiotherapeutic treatment, physiotherapy exercises, massage.
What is dangerous myopia?
Most parents are frightened by the fact that the child wears glasses. Myopia itself is not a problem. The most important thing for myopia is the development of complications. In some cases, an enlarged eye leads to the development of retinal dystrophy.
Dystrophy - these are areas of a weakened and thinned retina, which sooner or later may lead to a more formidable complication - retinal detachment.This is already a serious problem and may be accompanied by significant loss of vision. Therefore, a child with myopia needs to examine the fundus every six months.
Unfortunately, in children under the age of 7, it is almost impossible to recognize the initial myopia with the naked eye. But if the vision is reduced by 70-80%, it already becomes obvious. The child often stumbles, climbs badly down the steps, starts to squint. Parents need to be aware that children often do not notice a reduction in vision, especially if this happens gradually. Therefore, even in the absence of complaints of the child should be shown pediatric ophthalmologist at least once a year. This will allow time to detect eye disease in your baby and develop individual tactics of follow-up management and treatment.
Stages of development. By the time of birth, the eye has all the membranes if embryogenesis (Table 3) proceeded normally. The eye of a newborn differs significantly in size, mass, histological structure, physiology, and functions from an adult's eye.
Stages of development. After the birth of the child, the visual analyzer goes through certain stages of development, among which there are five:
- formation of the area of the yellow spot and central fossa of the retina during the first half of the year of life; of the 10 layers of the retina, “four remain mostly - these are the visual cells, their nuclei and structureless border membranes;
- an increase in the functional mobility of the visual pathways — and their formation during the first half of the year of life;
- improvement of the visual cellular elements of the cortex and cortical visual centers during the first 2 years of life;
- forming and strengthening the connections of the visual analyzer with other analyzers during the first years of life;
- morphological and functional development of cranial nerves in the first (2-4) months of life.
The formation of the visual functions of the child occurs according to these five stages of development.
Eyeball. The eyeball (oculus bulbi) of newborns has a shape approaching spherical (Fig. 3). According to the average echobiometric data, its anteroposterior (sagittal) size is 16.2 mm; by the year it increases to 19.2 mm. by 3 years - up to 20.5 mm, by 7 - up to 21.1 mm, by 1 - up to 22 mm, by 15 years is about 23 mm and by 20 -25 - about 24 mm. The size and shape of the eyeball to a certain extent depend on the type and size of one or another type of ametropia (myopia, hypermetropia, emmetropia). These variants can be hereditarily determined. Knowledge of the size of the eye is of great importance in assessing the type and stage of pathology (congenital glaucoma, myopia, etc.).
The outer shell, or capsule, of the eye is represented by a dense and rigid tissue, 9/10 is made up of an opaque fibrous part of the sclera and 1/10 of the transparent part is the cornea. The capsule-eye is similar in structure to the dura mater; it performs a protective function, determines the constancy of the shape, volume and, to a certain extent, the tone of the eye, is a skeleton for the attachment of the eye muscles; the capsule is pierced by the vessels and nerves, as well as the optic nerve.
Cornea. The cornea (cornea) is the main refracting structure of the eye (Fig. 4). It is transparent, smooth, shiny, has a mirror surface, spherical shape, does not contain vessels, is permeable, highly sensitive. The temperature of the cornea in the open palpebral fissure is about 20 ° C. The cornea width, or horizontal diameter, in newborns is on average 8–9 mm; by the year — 10 mm; by 11 years — 11.5 mm, which almost corresponds to the diameter of the cornea in (adults. Corneal growth, an increase in its size occurs due to stretching and thinning of tissue.The thickness of the central part of the cornea decreases on average from 1.5 to 0.6 mm, and on the periphery from 2.0 to 1.0 mm. The radius of curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea of a newborn is on average 7.0 mm , with age, some of its flattening occurs — and for years, the curvature averages 7.5 mm, as in adults. s. a healthy cornea curvature ranges from "6.2 to 8.2 mm, which is basically consistent with the type and size of clinical refraction.
The refractive power of the cornea varies depending on "age inversely proportional to the radius of curvature: in children in the first year of life, it averages 46 dptr, and by 7 years, as in adults, it is about 44 dptr. The refractive power in the vertical meridian is almost always 0.5 diopters more than the horizontal, which causes the so-called physiological astigmatism.
The surface layer of the cornea - Anterior epithelium (flat, multi-layered) - is essentially a continuation of the conjunctiva. Its two surface layers regenerate well and quickly in case of damage, leaving no cloud. The epithelium has a protective function and is a regulator of the water content in the cornea. It in turn protects it from the influence of the external environment by the so-called liquid, or precorneal, layer.
Under the epithelium of the cornea is located and loosely connected with it the anterior border membrane (bowman shell); it is structureless, inelastic, with damage it is not capable of regenerating, therefore, turbidity remains at the site of damage.
Stroma (own, the main substance) of the cornea is located under the anterior border membrane and merges with it without a pronounced border. This is the most important and massive layer with a thickness of up to 0.5 mm.
Behind the stroma lies the posterior marginal membrane (Descemet's membrane); it is very durable, elastic, regenerates in case of damage. To the periphery, the thickness of this membrane increases, in the area of the limbus it becomes diffuse and takes part in the formation of the trabeculae anterior chamber angle.
Inside the cornea is covered with endothelium. It consists of a single layer of prismatic hexagonal cells, it regenerates quickly in case of damage. Like the outer and inner border membranes, the endothelium performs a barrier function, participates in the formation of the trabecular apparatus of the anterior chamber angle.
The cornea contains about 18% of the definitive collagen of mesenchymal origin, about 2% of mucodolysaccharides, proteins (albumin, globulin), lipids, vitamins C, B2, etc., and up to 80% of water.
Nutrition of the cornea is carried out mainly due to the thick perilymbalous circulatory plexus. To a certain extent, the viability of the cornea is caused by the penetration of nutrients from the moisture of the anterior chamber.
Sensitive innervation of the cornea is carried out by the trigeminal nerve. The number of nerve endings is especially large in the surface layers, which causes its very high sensitivity.
In the first months of a child’s life, the cornea is insensitive due to the functional development of the cranial nerves that has not yet ended. During this period, particularly dangerous hit in the conjunctival sac. foreign bodieswhich do not cause eye irritation, pain and anxiety of the child and, therefore, can cause severe damage to the cornea (keratitis) until its destruction. In this regard, during the first year of the child's life, the doctor in the process of pediatric patronage should often carry out a thorough examination of the conjunctival sac and cornea. In a one-year-old child, the sensitivity of the cornea is almost the same as in an adult.
Trophic innervation of the cornea is provided by trophic nerves present in the composition of the trigeminal and facial nerves. The sympathetic nervous system is also involved in the regulation of the corneal metabolism.
Microphthalmos - a rare eye disease, characterized by a decrease in the size of the eyeball. Most often the problem is congenital and easily diagnosed. Determining its presence is important at any age and at any stage, since it is important to know what consequences it can cause and whether it is possible to get rid of it.
As a rule, ophthalmologists diagnose microphthalmos in case the length of the eyeball axis is less than normal. In this case, it usually does not exceed twenty-one millimeters in an adult and nineteen in a child. In many cases, against the background of the pathology is observed until its complete loss.
 Microphthalmus is a reduction in the size of the eyeball. Usually combined with eye defects
Microphthalmus is a reduction in the size of the eyeball. Usually combined with eye defects Causes
Among the main causes of microphthalmos are pathological processes in the womb. They can be inflammatory and degenerative in nature and often occur during the development of infectious diseases. Most often the disease is inherited in a dominant way.
 The disease can also be acquired. Among the main reasons in this case:
The disease can also be acquired. Among the main reasons in this case:
- Toxoplasmosis;
- Surgery on the organs of vision in childhood;
- Retrolental fibroplasia;
- X-ray irradiation in childhood.
Symptoms
The most pronounced symptom of the disease is a different size of the eyeball, different from the norm. In addition, pathology often causes the following symptoms:

In some cases, along with microphthalmia, other developmental pathologies can be observed.
In connection with the complex nature of developmental pathologies in a child, in the event of at least one, it is recommended to carefully monitor and periodically check the patient for the presence and progression of others.
Possible complications
In the event that the development of the disease is not stopped in time, there may be a high probability of complete loss of vision. Therefore, timely diagnosis is necessary, especially in the early stages. In the advanced degree of progression, the disease can seriously impair the appearance.
Treatment
Far from all cases, microphthalmic treatment can be effective. However, in the early stages of the progression of pathology can be stopped. If the patient completely loses his sight, he is offered cosmetic prosthetics. At first, a correction with telescopic glasses is usually shown. 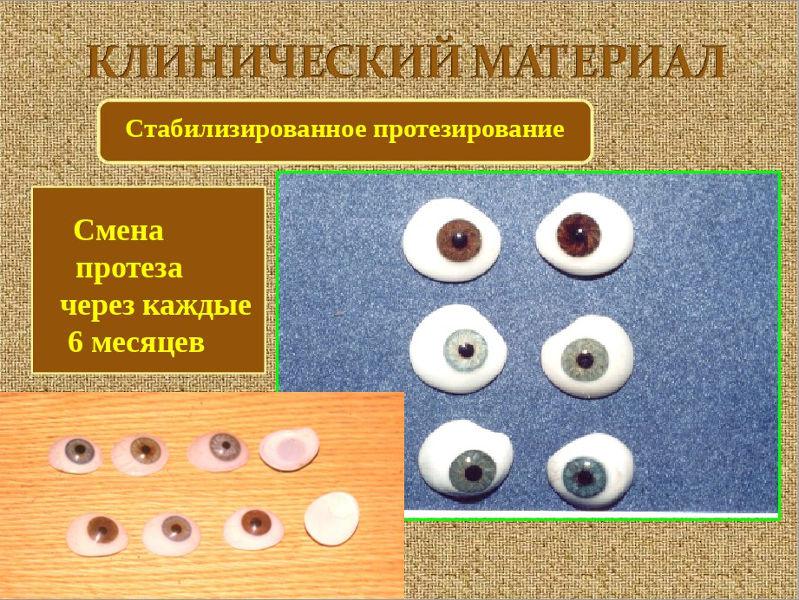
Medication method
Medicines in the treatment of microphthalmia are used only as an additional means. So, in this case, apply antiseptic solutions:
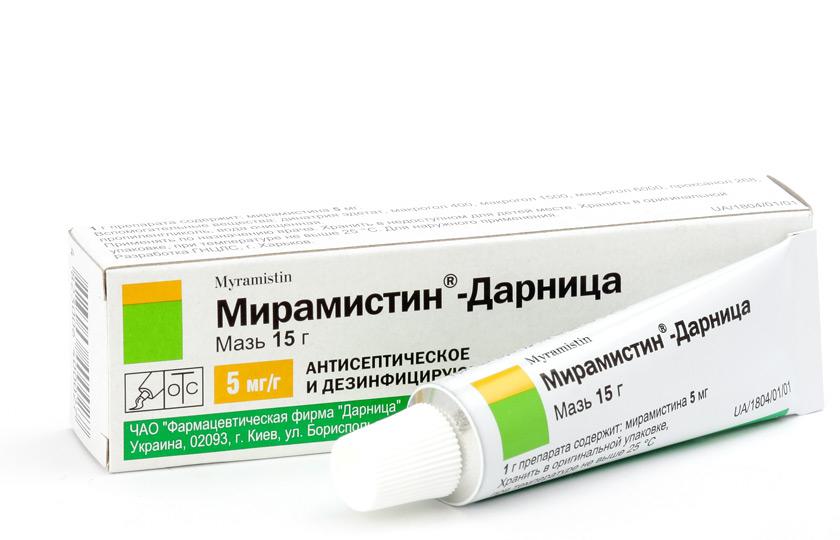
When wearing the prosthesis solutions must be used with caution. For denture eye drops not recommended.
Surgical
Surgical treatment of the disease, as a rule, is prescribed not earlier than the age of seven to eight years. It is carried out in the presence of glaucoma, retinal detachment and cataract. It is also possible to perform plastic surgery in order to improve the appearance with the subsequent installation of the prosthesis.
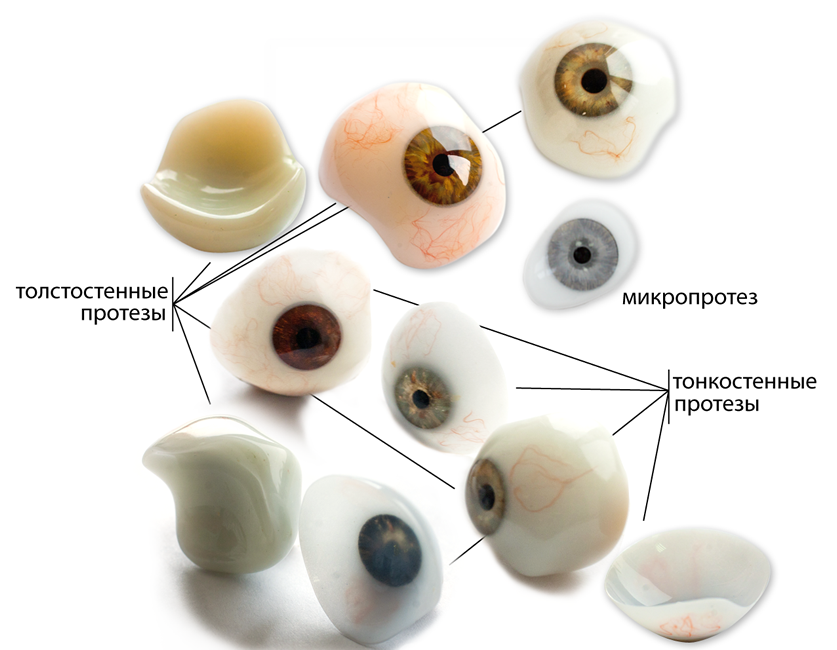
Prevention
The main preventive method to prevent the development of microphthalmia is to periodically visit the hospital and monitor with an ophthalmologist. AT agen analysis of each stage of the disease and changes in the organs of vision, which it generates.
To avoid the appearance of congenital microphthalmia, during pregnancy it is important to observe diet, take care of the general health of the body, as well as be observed at the doctor. After the birth of a child, periodic examination by doctors of all specializations, including an oculist, is necessary. This will help to avoid the possible causes of the appearance of pathologies.
Video
findings
Microphthalmus is one of the serious pathologies of the organs of vision that are almost not amenable to treatment with full restoration of functions. Nevertheless, the prevention of this disease is possible even before the birth of a child, as well as in early childhood. In case of eye damage with this ailment, treatment is reduced to stopping the progression of symptoms, as well as improving the patient's appearance with the possibility of prosthetics.
The eyeball of the newborn and during the first years of life is relatively large in relation to the whole body.
The most intensive growth of the eyeball is observed during the first year of a child's life. By two years, the eyeball is increased by approximately 40%, and by the year 20-21 - by 1.5 times compared with a newborn. A newborn eye weighs 2.3 g, and in an adult it is heavier by more than 3 times - 7.5 g. Thus, in a newborn the mass of both eyes in relation to body weight is 0.24%, and in an adult person only 0.02%.
Then the growth of the eyeball slows down somewhat, from about 12-14 years of age it again grows intensively up to 20-21 years.
The anterior chamber of the newborn's eye is shallow and normally is no more than 2 mm, reaching a depth of 3 mm, as in an adult in the first months of life with the onset of active functioning of the choroid.
Dynamics of growth and development of the cornea
In newborns, the cornea diameter averages 9.4 mm, gradually increasing to 11-11.5 mm, i.e., to the size of an adult. By 1 year of life, it reaches 11.25 mm. The formation of the thickness and curvature of the cornea ends in the second year of a child's life. The refraining power of the cornea in a newborn is more than 50 diopters and decreases by the next 3-5 years. The change in the refractive power of the cornea is associated with its flattening and increasing the radius of curvature. In a newborn, the curvature of the outer radius of the cornea is normally about 7-7.3 mm, and in an adult - 7.8-8.0 mm. In adults, emmetropic cornea diameter is on average 11.6-11.7 mm. The total area of the cornea on its surface is 1.3 cm2, which is 7% of the entire plane of the surface of the outer capsule of the eyeball. The total mass of the cornea is about 180 mg. The ratio of the area of the anterior surface of the cornea and the total surface of the outer capsule of the eyeball with a diameter of 24 mm corresponds to 1: 15.6.
The average radius of curvature of the cornea reaches 8 mm, and in men it is 1.5% more than in women. The cornea thickness, obtained on the basis of in vivo studies, by the age of 55 in the central zone is 0.539 mm, and at the periphery - 0.676 mm. The thickness of the cornea between the center and the periphery ranges from 0.1 to 0.3 mm. Optically, the cornea refracts the rays of light as a strong convex lens, exceeding the refractive power of the lens by more than 2.5 times. The refractive power of the cornea is more than 40 dptr, the lens - about 20 dptr at rest in accommodation.
Dynamics of growth and development of the lens
The newborn lens is almost spherical in shape, very soft texture, transparent and colorless. During the whole life, new lens fibers enclosed in the closed space of the lens bag (capsules) grow and are added. This leads to a gradual increase in the relative density of the lens, its mass and volume. The relative density of the lens at the age of 20 is 1,034, at 50 years - 1.072, at 90 years - 1.113.
In adults, the equatorial diameter of the lens reaches 9-10 mm, the sagittal size is 3.7-5.0 mm. The thickness of the front capsule is 11-15 microns, the back - 4-5 microns. The inner surface of the anterior capsule contains a single-layer, transparent cubic epithelium, the posterior epithelium capsule is devoid. The intensity of the yellowish shade of the lens increases with age.
By the age of 40-45, the nucleus of the lens becomes dense, it loses its elasticity. By this time, there is a significant weakening of accommodation and phenomena of presbyopia appear. By the age of 60, the ability to accommodate is lost almost entirely due to pronounced sclerosis of the nucleus of the crystalline lens - facosclerosis. During this period of life, a thickening of the anterior lens capsule up to 17 microns is observed, and in the paracentral zone up to 25 microns. The equatorial (enzymatic) zone does not undergo significant changes in its thickness due to age.
One of the most common diseases in children is myopia, or myopia. Most often, it manifests itself at school age of the child, which is usually associated with an increased load on the eyes.
In the first year of life, myopia appears in 4-6% of children. Due to the growth of the eyeball in preschool children, myopia is less common, but in children of 11-13 years old, myopia is observed in 14% of cases.
Myopia may be congenital or acquired.
The direct cause of myopia is a violation of the proportion between the strength of refraction (refraction) and the length of the anterior-posterior axis of the eye.
Due to the violation of the ratio of the size of the eye and refraction, the image of objects falls not on the retina (as it should), but in front of it. Therefore, this image will be blurry. And only negative lenses or the approach of an object to the eye can give an image on the retina, that is, a clear one.
Risk factors for the development of myopia are:
- heredity;
- prematurity of the fetus;
- congenital anomaly of the eyeball, lens or cornea;
- congenital glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure);
- increased visual loads;
- visual hygiene disorders;
- infectious diseases (including frequent, pneumonia);
- poor nutrition of the child;
- some common diseases (diabetes, Down syndrome, etc.).
The hereditary factor is of great importance for the development of myopia, but it is not the disease itself that is inherited, but a predisposition to it. Moreover, it is significantly increased if myopia is present in both parents.
Congenital myopia may not progress if there is no hereditary predisposition (weakness or high extensibility of the sclera). But, as a rule, they are combined and lead to pronounced loss of vision and constant progression. These irreversible changes in the eye can even cause disability. Myopia also develops in the case of a combination of glaucoma and sclera weakness.
In rare cases, babies have temporary, transient myopia. 90% of full-term babies have “farsightedness with a margin” of 3-3.5 diopters. Hyperopia is therefore the norm for babies. This is due to the small size of the eye: the anterior-posterior axis of the eye in an infant is 17–18 mm, by 3 years it reaches 23 mm, in adults it is 24 mm.
It is seen that the largest growth of the eyeball occurs up to 3 years, and its full formation is achieved in 9-10 years. During this period, the “reserve” of farsightedness is spent, and eventually normal refraction is formed.
But if at birth there is a farsightedness of 2.5 diopters (and less) or normal refraction in general, then the probability of the development of myopia in a child is very high: this “stock” is not enough to grow with the age of the eyeball.
In premature babies, myopia develops in 30-50% of cases.
But still more often, children develop acquired myopia, progressing during the years of study at school.
This is facilitated by:
Some parents mistakenly believe that glasses prescribed to a child contribute to the progression of myopia. This is not true. Myopia will increase only with incorrectly matched glasses.
Symptoms
 A child with myopia decreases visual acuity, it is difficult for him to examine objects that are far away.
A child with myopia decreases visual acuity, it is difficult for him to examine objects that are far away. The first sign of myopia in a child is a decrease in visual acuity at a distance, which causes the child to squint. Sometimes this visual impairment is temporary, transient, reversible.
Symptom of myopia is also rapid fatigue of the eye when reading, when viewing any objects close. Children can try to bring their eyes to the text while reading or writing.
The myopia detected at this stage can be stopped, therefore it is so important to show the child to an oculist regularly, regardless of the presence of complaints.
Divergent strabismus in a 6-month-old baby (or older) may also be a manifestation of myopia. In this case, consultation with an oculist is also necessary.
After a year, the frequent blinking of the baby and his desire to bring any subject closer to the eyes can be evidence of myopia.
At school age, children may not see the text written on the blackboard, and from the first grade they see better. Near vision remains normal. The guys also note rapid eye fatigue.
Such a condition can cause not only myopia, but also a spasm of accommodation (that is, with a spasm of intraocular muscles that regulate the refractive power of the eye). A spasm can be a manifestation, increased nervous excitability, or appear when the rules are violated during reading (insufficient lighting, incorrect posture, etc.).
The appearance of "floating flies" before the eyes may indicate a complication of myopia - destructive changes in the vitreous body.
There are such types of myopia:
- physiological: appears in the period of growth of the eye;
- pathological: is actually myopic disease; differs from physiological myopia by a progressive course;
- lenticular: associated with high refractive power of the lens when it is damaged due to congenital cataracts or the effects of certain drugs.
In the course of myopia is not progressive and progressive.
The severity of myopia is:
- weak (up to 3 diopters);
- medium (3-6 diopters);
- strong (above 6 diopters).
Diagnostics
- Survey of the child and parents: allows you to find out the presence of complaints and the timing of their appearance, during pregnancy and childbirth, previously transferred and comorbidities, family or hereditary factors, changes in visual acuity in dynamics, etc.
- Examination of the child includes:
- external eye examination: allows determine the position and shape of the eyeballs;
- examination using an ophthalmoscope: determining the shape and size of the cornea, assessing the anterior chamber of the eye, lens and vitreous body, examination of the fundus; with myopia around the optic nerve head, a myopic cone is detected, atrophic changes in the fundus, pigmentation and hemorrhages, and even retinal detachment with high myopia can be observed;
- skiascopy (using an ophthalmoscope and skiascopic ruler) to determine the type of refraction and the degree of myopia;
- Ultrasound helps to determine the size of the anterior-posterior axis of the eye, to detect the presence of complications;
Up to 3 years, only the named methods are used, but the results are compared with previous data (at 3 and 6 months).
From the age of 3, visual acuity is additionally checked using special tables. With reduced visual acuity lenses are selected for correcting distance vision: this allows you to determine the degree of myopia.
It is possible to replace the skiascopy with autorefractometry: after a 5-day atropinization of the eyes (instillation of the atropine solution into the eyes), examination with a slit lamp. 2 weeks after atropinization, the necessary corrective lenses are re-determined.
Schoolchildren are at risk for developing myopia, so their visual acuity should be checked annually. Reduced visual acuity in them can be both a manifestation of myopia and accommodation spasm.
Therefore, re-determination of both visual acuity and refraction is carried out after a 5-day atropinization. In the case of accommodation spasm, normal refraction and visual acuity are detected. In this case, treatment is prescribed and an examination by a neurologist is recommended.
In case of myopia, a repeated examination will again reveal a violation of refraction and visual acuity, and the correction is achieved only with the help of negative lenses. Myopia in schoolchildren is often mild or moderate. It usually does not progress and does not lead to complications.
But such children should be observed by an oculist every 6 months in order not to miss the progression of the process and the development of complications (atrophic changes of the retina and even its detachment). Therefore, the results of each of the next inspection should be compared with previous data.
An increase in myopia by 0.5–1 diopters per year indicates a slow progression of the process, and more than 1 diopter indicates a fast progression. It can lead to a sharp decrease and even to a complete loss of vision, irreversible complications in the retina (hemorrhages, tears, detachment, destructive changes). Usually, progression occurs from 6 to 18 years.
Treatment
 Proper selection of points and their continuous use helps to slow the progression of the disease.
Proper selection of points and their continuous use helps to slow the progression of the disease. To cure myopia in childhood is impossible. You can get rid of it after 18-20 years. Treatment depends on the degree of myopia, the type (progressive or not progressive), the existing complications.
The goals of myopia treatment in childhood:
- slowing or stopping progression;
- prevention of complications;
- vision correction.
With progressive myopia, the sooner treatment begins, the greater the opportunity to save the child’s sight. Amplification of myopia less than 0.5 diopters per year is permissible.
In the treatment of myopia such methods are used:
- eye gymnastics;
- vision correction;
- orthokeratology method;
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy treatment;
- general body strengthening and correction of posture disorders;
- surgical treatment.
At the initial stage of the development of myopia, daily exercises of a special eye gymnastics , which will relieve stress and eye fatigue. There are many techniques for strengthening the intraocular muscles. An optometrist will help you choose a specific set of exercises. Such exercises are not difficult, they should be performed at home at least 2 p. in a day.
Some doctors conduct training of the ciliary muscle in the eye cabinet: negative and positive lenses are alternately inserted into special glasses.
With weak myopia, the doctor sometimes selects “relaxing” glasses with weakly positive lenses. Computer programs are also used to relax accommodation at home.
Special laser-vision glasses are also used (Laser Vision). These perforated glasses are called "training glasses": they give the desired load to the weakened muscles of the eyes and relaxation overly tense. You need to use them for 30 minutes a day. Can be used as a preventive measure for adolescents who spend a long time at the computer.
With the aim of vision correction The optometrist picks up glasses for the child - a traditional and common method of correction. And although they do not have a therapeutic effect, you should convince the child to wear glasses (or contact lenses for older children). Researches of experts in the USA and Europe testify, what exactly the wearing of glasses leads to the worst variants of a course of a myopic disease.
Glasses not only create comfort for the child, but also reduce eye strain, which reduces the progression of the disease. In the case of congenital myopia, glasses should be assigned as early as possible. With mild to moderate myopia, glasses are issued only for distance.
Constant wearing of glasses is necessary with high myopia and with progressive. Wearing glasses is also necessary for diverging strabismus.
Wearing contact lenses recommended for older children in case of significant (above 2 diopters) difference in refraction in both eyes, that is, in the case of anisometropia. Selection of lenses should be carried out by a specialist, as poor-quality optics and correction can aggravate myopia.
With myopia, it is necessary to change the glasses in a timely manner, because excessive stress on accommodation will contribute to the progression of myopia. The disadvantages of vision correction with the help of glasses are: the inconvenience in sports, limitation of peripheral vision, impaired spatial perception, trauma.
Correction with the help of lenses is more convenient, but the use of lenses is contraindicated in the event of an infectious disease. The disadvantage is the possibility of injury to the eyes if used improperly or infected when putting on non-sterile lenses.
Currently applied correction lenses in the night mode - orthokeratology method or corneal refractive therapy - use for 6-8 hours of special lenses that cause a change in the shape of the cornea (flatten it) for up to 2 days. During this period, 100% vision without glasses is achieved. Lenses are used at night, during sleep, so this method is called night vision correction. Then the shape of the cornea is restored again.
The result of night correction is close to the laser (changes the refractive power of the cornea) and differs only in the short duration of the effect, which is associated with the constant renewal of the cells of the cornea.
The safe method of night correction can be used in children from 6 years. These special lenses not only completely remove the accommodation spasm in children, but also inhibit the development of myopia and its progression.
To reduce the tension of the intraocular muscles, eye drops are sometimes prescribed (usually Atropine) by a 7–10-day course. But self apply drug treatment it does not follow. In addition, with weak myopia, vitamin complexes containing lutein can be used. For example, LUTEIN-KOMPLEX® Children's, specially developed for eye health, is a multicomponent product, which consists of substances necessary for the normal functioning of the organs of vision of a school student from the age of 7: lutein, zeaxanthin, lycopene, bilberry extract, taurine , vitamins A, C, E and zinc. A combination of biologically active components carefully selected to meet the needs of the organs of vision protects the eyes of the child, which is especially important to do, starting with 7 years old, when the first serious visual loads begin in elementary school. and reduces the risk of eye diseases.
For the prevention of complications and progression of the process, nicotinic acid, Trental, calcium preparations are prescribed. In the initial manifestations of dystrophy, Emoksipin, Ditsinon, Ascorutin are used. In some cases, it is advisable to use resorptional drugs (Lidase, Fibrinolizina, Kollalizina).
From physiotherapeutic methods, the use of Dibazol in the form of electrophoresis gives a good effect. The so-called “myopic mixture” can also be administered in the same way: diphenhydramine, novocaine and calcium chloride. In some cases, effective reflexology.
Physiotherapeutic devices for home treatment are also used to improve vision. The principle of their action is different: “massage the pupil” (narrowing and widening it), improving the blood supply to eye tissues, electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, etc. Perhaps alternate treatment with the help of various devices.
One of the effective devices allowed for use for children over 3 years old is called "Sidorenko glasses". The device combines the following methods of exposure to the eye: pneumomassage, phonophoresis, color therapy and infrasound. It has no side effects, and in many children it allows to avoid surgery for progressive myopia. The device is widely used in the complex treatment of children.
As restorative treatment observance of the daily regimen, dosing of visual loads (including regulated time watching TV programs and computer lessons), vitaminized balanced nutrition of the child, daily walks in the fresh air, and swimming are recommended. With a high degree of myopia, and even more with the appearance of complications, active sports are contraindicated (running, jumping, etc.). Children with this pathology should choose a special set of exercises.
The indications for him are:
- myopia 4 diopters and more;
- rapid progression of the process (more than 1 diopter per year);
- rapid growth of the anterior-posterior axis of the eyeball;
- lack of complications from the fundus of the eye.
During the operation, the posterior pole of the eye is strengthened, which does not allow the eye to grow further. To improve the blood supply to the sclera, 2 intervention options are possible: hemming a graft from a donor sclera (silicone or collagen) or introducing a liquid suspension from crushed tissue at the posterior pole of the eyeball. The operation does not lead to a cure, it only reduces the progression of the disease.
Laser vision correction is the safest type of operation for myopia, which lasts about 60 seconds under local anesthesia, and provides a lifelong effect, eliminating the need to use glasses or lenses. But, unfortunately, such operations are contraindicated for children (under 18).
The best result in myopia gives the use of all methods of conservative treatment in the complex, and with rapid progression - in combination with surgery.
Forecast
Weak and moderate myopia in schoolchildren have a favorable course: it does not progress and does not give complications, it is well corrected with glasses.
A high degree of myopia leads to a decrease in visual acuity even with lens correction.
Lack of correction of myopia may be fraught with the appearance of diverging strabismus.
With progressive and congenital myopia, with the occurrence of complications, especially on the part of the retina, the prognosis is poor, there is a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Prevention
From a very young age, one should teach a child to observe when reading a few simple rules:
- the distance from the book to the eyes is not less than 30 cm;
- follow the correct posture at the table;
- do not read lying down;
- read only with sufficient light.
Care should be taken to ensure that the table (desks) grows in size. We must pay attention to the chair: legs bent at the knees at an angle of 90 degrees should reach the floor. The light when reading, drawing and writing should always fall on the left for the right-handed person and the right for the left-handed person. Even in the children's playroom, good lighting should be provided.
Before starting school, you should consult an ophthalmologist and clarify at which school desk the child should sit, if he needs eye correction.
It should reasonably limit the time watching TV and playing games on the computer. Do not allow watching television in the dark.
A balanced diet and the periodic use of vitamin complexes for the eyes will help not only in the treatment, but also in the prevention of myopia in children.
Resume for parents
Myopia in a child can lead to the development of a persistent reduction in visual acuity and the occurrence of serious complications. Much depends on the timely correction of vision and treatment. Therefore, it is important every year (and children from the risk group 2 times a year) to visit with the child an oculist.
In the event of myopia, it is necessary to immediately follow all the recommendations of the doctor to eliminate the rapid progression of the disease, to avoid operational intervention.
There are several methods of conservative treatment of myopia. Even gymnastics for the eyes can have a good effect with its regular use.
If the child is prescribed glasses, it is necessary to control the compliance of the lenses in them and to change them in a timely manner.
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0