Blurred vision may occur as a result of lesions of the retina, optic nerve, optic tract, external cranial bodies, visual radiance and projection of the visual cortex.
Retinal lesions can lead to arcuate cattle that are directed toward or emanating from the blind spot. If the disc area and the blind spot are affected, a central or centroceral scotoma occurs, which, as a rule, is a consequence of damage to the optic nerve (multiple sclerosis, compression of a nerve by a tumor, etc.). Bilateral and fairly symmetrical central and centrocecal scotomas indicate toxic damage (methyl alcohol, chronic alcohol intoxication, etc.). For optic-chiasmatic arachnoiditis, the characteristic but concentric narrowing of the visual fields, sometimes to tubular vision.
The most typical types of loss of visual fields in the pathology of the nervous system, namely half of the visual fields, are found in cases of damage to the optic tract, external articular body, visual radiation and projection of the visual cortex - homonymous hemianopsia, i.e. loss of the same half of fields the view of both eyes: the left - with a lesion in the right hemisphere, and the right - in the left.
Hemianopsia
Heteronymous hemianopsia, i.e., affection of various named fields of vision (on one eye of the left, on the Drug of the right), occurs much less frequently, and the bitemporal (loss of the temporal halves) is noted mainly in tumors of the pituitary-chiasm areas, and the binasal (prolapse of the nasal polovines) - with bilateral aneurysm of the intracranial portion of the internal carotid artery. When hemianopsia there is a clear vertical dividing line. Along with complete hemianopia, incomplete approaching quadrant also occurs: if a spur sulcus is damaged, visual field defects are identical on both sides, and as a rule, the optic tract, lateral articular body, and visual radiance are asymmetric.
Homonymous upper quadrangular hemianopsy is most often encountered during volumetric processes in the temporal lobe (compression of a portion of visual radiance fibers, namely, those coming from the lower quadrants of the retina). Constriction of the predominantly lower quadrants of the field of vision can occur with compression of fibers originating from the upper quadrants of the retina, which happens with deep tumors of the parietal occipital localization. Persistent cortical blindness arises as a result of ischemia in the pool of both posterior cerebral arteries and is characterized by anosognosia, i.e., the unconsciousness of its defect (Anton's symptom), while pupillary reflexes remain intact.
Micropsia and macropsia
Qualitative changes in vision, expressed in the apparent increase in visible objects (macropsy) or, on the contrary, their decrease (micropsia), in distortion of space or proportions of their body, are found in lesions of the parietal lobe, especially the right hemisphere, in tumors, encephalitis, and . p. (Interparietal syndrome).
Epilepsy
Phenomena in the form of rainbow circles before eyes, sparks, shimmering spirals, etc., are characteristic of a visual aura in migraine. In these cases, a migraine attack develops in no more than 60 minutes, although there may be isolated manifestations of aura without pain. Short-term (minute) similar attacks may also be a manifestation of occipital-lobar epilepsy and may be accompanied by headache. The derealization of the vision (the state of the already seen, never seen) is a form of a complex partial seizure with temporal epilepsy.
The classic Argail-Robertson symptom is considered to be the classic pathological pupil phenomenon - the preservation of the pupils' reaction to convergence and accommodation in the absence of it into the light, which is pathognomonic for neuro-lues. Material from the site
It should be remembered that the sluggish reaction of the pupil to light may be the result of a sharp decrease in the sharpness of vision. In case of amaurosis, the lack of reaction of the pupils to light indicates damage to the optic nerve. When the optic tract is affected, the reaction to light from the “blind” half of the visual field falls out (it is examined by a special lamp), which is called the hemianoptic pupil reaction.
Impairment of visual radiance and projection of the visual cortex, even if it leads to blindness (with bilateral lesion), is not accompanied by loss of the pupil reaction to light, since the closure of the afferent part of the pupil reflex arc to light occurs below, in the pretectal region midbrain (recall that the efferent part of the arc begins from the small cell parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotor nerve).
One of the most important feelings that the human body is endowed with is vision. Thanks to him, a person acquires the ability to see the world around him, to know it, to learn and change it according to his desires and needs. A person who is deprived of vision is partially isolated - visual images are not accessible to him, he is limited in perception. Such a person is not destined to see the smiles of his family, spring flowers and autumn leaf fall, snow, greens of young grass and a clear summer sky. A person with poor eyesight or completely blind is limited in his personal and professional activity. He can not engage in many sports, and poor eyesight often vetoes the desire to become a military man, a pilot, a sailor, a driver, or many other specialties.
Even worse, visual impairment is found in a small child. The more serious these violations, the harder it will be to learn the world, learn and develop.
But for an adult, visual impairment carries many unpleasant moments. The need to wear glasses, extremely unpleasant eye diseases, a strong distortion of the image that interferes with seeing, reading and writing normally - all these are mainly the consequences of our high-tech computer lifestyle. The reasons for the fact that a person complains of blurred vision, many, but the vast majority of them relate to acquired diseases and conditions.
Poor vision is a very broad generalized name of the state in which there is a visual impairment, leading to a change in the perception of the shape of the object, the assessment of the distance to it. When vision deterioration occurs, a person complains about the lack of clarity and sharpness of the image, objects "blur", lose their contours, become muddy. The patient can not make out the inscriptions, numbers, symbols, but if his eyesight has deteriorated, he often has difficulty in moving and using ordinary household accessories.
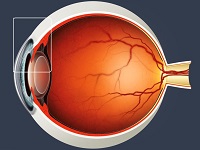
Naturally, the decrease in visual acuity significantly affects the quality of life of the patient. Moreover, the degree of negative impact increases with decreasing vision. Since there are many reasons for such a condition, it is important to accurately diagnose and, as far as possible, to cure the underlying disease or to eliminate what causes visual impairment.
It is possible to classify the reasons for the deterioration of vision in different ways. If you focus on what causes it, you can apply the following division:
- Pathology of organs of vision inborn character. They may be genetically determined, that is, be hereditary, or they may appear due to various violations of the formation of the fetus during intrauterine development.
- The pathology of the elements of the organs of vision acquired character, the cause of which may be eye disease Diseases of various nature, including infectious ones, can lead to a decrease in the quality and visual acuity.
- Visual impairment caused by injury to the eyes, nearby organs, brain. Falling vision is often the result of severe concussions, blows to the head, falls, eye damage with a variety of objects, after a polytrauma.
- Visual impairment associated with external exposure: thermal, chemical and radiation. This includes burns caused by chemical agents, fire or flammable liquids.
- Visual impairment caused by certain pathologies or diseases of internal organs, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
- External effects of a non-physical property: reading books with small print, in poor light, lying in a moving vehicle, watching television for too long, working with a computer, especially various games, using electronic devices (smartphones, tablets, e-books).
- Age changes. The older a person is, the higher the risk for him of the appearance of various eye diseases, as well as reduced visual acuity. Most people develop so-called presbyopia with age, that is, age farsightedness. That is why many middle-aged people are free to navigate on the street, but they are forced to use glasses to read, watch television or do small jobs.

The classification of visual impairment does not always have clear boundaries, since some problems may be interrelated or flow from one another.
Sometimes a person may show symptoms of rapid visual impairment. This can indicate very dangerous injuries in the body, for example, methanol poisoning. At the same time there is a risk of not only irreversible damage to eyesight or complete blindness, but also death. With the appearance of threatening symptoms, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help, call an ambulance.
In case of visual impairment, people often complain that they cannot focus on the outlines of objects. Most often this indicates the presence of a specific problem with the formation of two foci, which is called astigmatism. It accompanies many visual defects, and can occur with hyperopia and myopia. The defocused image arises from the fact that the optical focus is not formed on the retina, but in front of it. At the same time, the eye receives not a clear, but a blurry signal, the image takes on a scattered look, and the vision can deteriorate dramatically.

One of the most frequent problems with visual acuity among today's youth is too frequent use of a computer. If a earlier cause Falling of view was the flickering of a computer screen, now overfatigue has an increasing influence on the sharpness of the eye - many people, mostly children and teenagers, do not deviate from computers for hours. Monotonous actions and fixation of the gaze on the screen, slowing down the blinking and drying of the mucous membranes of the eyes often cause the vision to gradually deteriorate.
Types of vision problems
Poor vision is a serious problem, it should be disturbed not only by the fact that a person cannot consider any details, but also by the fact that it can affect the condition of other organs. Prolonged fatigue of the eye entails headaches, vascular spasms of the brain, dizziness, a tendency to fainting, migraines, and many other extremely dangerous and unpleasant conditions and diseases. If vision deteriorates, it is imperative to look for the reason why visual distortions appear, and treat them. This will help not only prevent a decrease in visual acuity, but also reveal some other diseases.

The classification of existing visual impairment varies from country to country, but it is mainly divided according to the degree of visual acuity of the eye that sees better:
- Almost the norm - 20/30 - 20/60.
- Mild visual impairment - 20/70 - 20/160.
- Severe form of falling vision - 20/200 - 20/400.
- Deep vision loss - 20/500 - 20/1000.
- Almost complete blindness - over 20/1000.
- Total blindness - the lack of susceptibility to light.
It is also important to consider the possible loss of peripheral vision.
Types of visual impairment also leave their imprint on the problem of determining the cause of this condition, as there may be a combination of several factors at once, for example, the presence of such a congenital defect in the eye structure, such as injuries, which led to a decrease in visual acuity, as well as diseases of the organs of vision. To "get to the bottom" of the reasons why the blurred vision occurred, you will have to go through a lot of different examinations and pass a lot of tests.

The most common problems include eye ametropia. This concept includes farsightedness. A huge number of the planet’s population has various forms and degrees of ametropia. Ideal vision - a great rarity, most often the vision is about 0 5, that is, the minimum deviation from the norm. Doctors believe that optics before 1 do not need correction, that is, wearing glasses or contact lensesotherwise amblyopia may develop, or "". With him, the eye, whose functions partially compensate for glasses, begins to "be lazy" to work and vision continues to fall.
Common types of visual impairment are complemented by a huge list of diseases. Sometimes a temporary loss of vision is associated with injury. For example, when fainting, vision is not restored immediately, the patient first begins to hear, and only then the opportunity to see comes back to him. In a number of diseases, only a disturbance of twilight vision appears, that is, perception decreases as the contrast of surrounding objects decreases.
A little apart is the loss of vision in diabetes mellitus, or diabetic retinopathy. This disease develops gradually and over time can lead to complete blindness, so it is so important to diagnose and treat diabetes in a timely manner. At risk are people with burdened heredity and having overweight, obesity, even if they do not yet have complaints about vision.
The reasons for the deterioration of vision, sometimes catastrophic, can be various diseases, for example, or clouding of the lens of the eye, and. The latter disease is incurable and gradually causes a strong decrease in visual acuity. Its development can only be slowed down with special drops and special techniques. The cataract is now successfully operated, replacing the lens with an artificial one and returning people to see well.

In recent decades, computer syndrome has become one of the most common causes of visual impairment. In the initial stages, it causes strong drying of the mucous membranes of the eyes, which is successfully corrected with special drops. This state is called by the radiation of a computer screen and the reflex slowing down of blinking. In this case, the eyes do not receive enough moisture and suffer from this. There is a feeling of "sand in the eyes", pain and soreness. Over time, with a large amount of computer pastime, vision weakens due to constant overloads. At the beginning of the process, a fall can be prevented by starting to give eyes a rest, dispense work with a computer, distract from it more often and use special eye drops.
Poor eyesight as a social problem
Visual impairment is gradually ceasing to be a private problem and goes to the state level. Because of people with poor eyesight, accidents occur at transport and at work, weak eyesight is threatened with errors in complex and important operations and actions, visually impaired people are at much greater risk than citizens with good eyesight. Children are particularly affected - they are deprived of the opportunity to engage in active sports related to stress, tremors or weight lifting.
Psychologically unstable personalities, which include adolescents and the elderly, reduced vision with a high risk of complete or partial loss of it often leads to the appearance of serious mental disorders, including the desire for suicide. The government must take measures to reduce visual acuity due to illness or injury, and to work with such patients not only experienced ophthalmologists, but also good psychologists, and sometimes psychiatrists are involved.

But to influence the computer syndrome under the power of the man himself. Parents should ensure that the child does not spend more than two hours a day at the computer screen, does not sit in the dark with the lights off. Adults, by virtue of their type of activity, are constantly loading their eyes, can also reduce the influence of a computer on vision. To do this, you can wear special glasses, use vitamin drops and “artificial tears”, and also often take your eyes off the screen, changing the focus of view. Then the words “I cannot consider what is written” will not become an unpleasant and painful discovery for you, and you will be able to maintain good vision until old age.
Poor vision reduces the quality of a person’s life. Defects of the optic organs are observed in the older and younger age groups. They suffer and many celebrities. Congenital eye diseases and other acquired diseases (cerebrovascular accident, Parkinson's disease) provoke a change in visual acuity and, in general, impaired vision. Dysfunction, organic lesions of one of them provoke visual impairment.
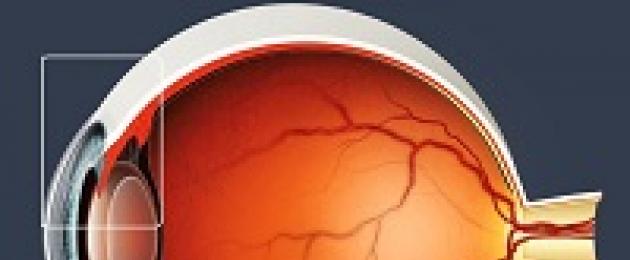
Our eyes are a very important and at the same time quite vulnerable organ. To understand why vision falls, it is necessary to know what the structure of the eye consists of.
The visual mechanism consists of eyeball and optic nerve. The optic nerve conducts visual impulses to the brain, the corresponding centers of which process and use the information obtained. The condition of these centers affects visual perception.
The structure of the eyeball (what it consists of):

- shell: retina, vascular mesh and fibrous layer (cornea, sclera). These are the inner, middle and outer layers respectively;
- the nucleus is represented by a gelatinous substance containing the vitreous body, the eye lens, aqueous humor; this is a complex structure.
The cornea is a film covering the eye outside. It is transparent, its functions are optical and protective. Sclera covers the eye from the inside. This substance is like boiled egg white. Some diseases are manifested by changes in the color of the sclera (for example, yellowing with hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver). Conjunctiva is the mucous structure of the eye. The iris has special muscles that shrink and dilate the pupils by adjusting the amount of light stimuli. The image is focused on the retina.
The retina and lens - the main optical parts of the eyeball, blurred vision, loss of vision are often associated with their defects.
In younger children, the eyes are more vulnerable due to not fully formed defense mechanisms.
Causes of pathological changes
Poor vision is congenital. Violation of intrauterine formation of the eye organs leads to the fact that the child is born with visual defects. Another part of eye diseases, loss of vision (blindness) are acquired in the process of life due to a number of factors. The activity of the eye organs is disturbed by various factors.
Causes of visual impairment:
- prolonged overloading of the eye organs, especially if the work activity is connected with the computer;
- atony of the musculature of the lens. The weakening of his muscles leads to the fact that his vision drops;
- conjunctival draining. Rare blinking during monotonous work in front of a computer screen or watching TV provokes dehydration, drying of the eye and weakening of vision;
- blood flow disorder. The proper functioning of the retina is directly dependent on the state of local blood circulation. Its changes cause visual impairment. The causes may be systemic diseases - vascular, neurological, metabolic (strokes, Parkinson's disease, diabetes mellitus);
- age-related changes in eye tissue in an elderly person. The photosensitive pigment, due to which visual images are perceived, is destroyed over the years. Aging and other parts of the eye, which causes a loss of vision;
- infections. It is considered especially dangerous for the youngest ones in infants - for newborns, the lack of timely treatment which provokes various visual defects, even complete blindness;
- mechanical damage, chemical and thermal burns of the eyes cause visual impairment, depending on their degree, absolute loss of vision may occur.
Inadequate rest, lack of proper sleep, the presence of bad habits, poor nutrition, contribute to pathologies.
There is a classification of visual pathologies by the age of people suffering from them (children, age), classification depending on the severity and nature of the changes (organic, functional), classification by origin (congenital, acquired, hereditary), etc.
Eye Pathologies
Myopia, hyperopia (hyperopia), astigmatism, cataracts, glaucoma are common pathologies that are accompanied by impaired visual function. Their common symptom is a decrease in vision. The first three are associated with impaired focusing of images; these vision problems often occur in younger schoolchildren.
- Myopia (or myopia) is characterized by poor visibility of objects at some distance. The harder the form of myopia, the worse a person sees objects located in the distance or even does not see them at all. The image is focused in front of the retina. Causes is a change in the corneal curvature, lengthening of the eyeball. Weakening of vision due to myopia tends to progress. Quite often, acquired myopia develops in younger students with the onset of school attendance, increased eye strain, as a result of which problems with vision occur. To correct poor eyesight, younger children use glasses, older ones have special lenses, prescribe eye exercises.
- Hyperopia is caused by impaired corneal curvature, an insufficient size of the eyeballs. The image is formed outside the retina. A person poorly distinguishes between pictures located near. Due to farsightedness, vision problems also often occur in schoolchildren.
- Astigmatism is caused by the deformation of the ocular surface. A healthy eyeball is round. When astigmatism is broken, its structure becomes oval. The irregular shape disrupts the focusing activity of the eye. Rays of light are projected at two points, because a person sees objects vaguely. If the pathology is not corrected in time, the eyesight drops sharply, and squint develops. Astigmatism tends to develop in younger children, often accompanied by other visual impairment (myopia, hyperopia).

Timely correction of these pathologies in younger children gives good results, the learning activity is almost not disturbed.
History reference. The systematic training of blind children in Russia, the intensive development of typhoid pedagogy began at the end of the XIX century.
How to deal with the disease? To stop the progression of the pathological process, apply a diet that improves visual ability. It is necessary to allocate a little time every day to take a child, as prescribed by a doctor, by visual gymnastics - a game form is useful. In some cases is a good method laser correction (after 18 years).
Today, wearing glasses for schoolchildren causes less discomfort, since this accessory is now in a trend, it is used by many stylish celebrities. Correction lenses lead to the restoration of impaired eye abilities.
When a cataract there is a change in the transparency of the lens, its clouding.
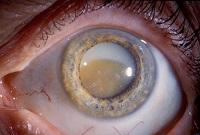
Causes: intrauterine infections, genetic, metabolic diseases. Acquired cataract people get sick, you can say that this is the most common eye disease of the elderly population. The progression of the disease is disappointing - an absolute loss of vision.
Modern ophthalmology offers surgical treatment of poor vision - lens opacities). The operation allows to partially or completely eliminate visual defects.
It is characterized by increased intraocular pressure. This is a dangerous disease that affects not only the elderly, but also representatives of the younger age groups. In adults and children, it is both an independent ailment and a symptom of others.
Varieties and forms of glaucoma, depending on the etiological factor:
- inflammatory;
- glaucoma resulting from a pronounced narrowing of the uveitic angle;
- corticosteroid (is a consequence of hormone therapy in this group);
- glaucoma associated with structural disorders, chronic inflammatory process.
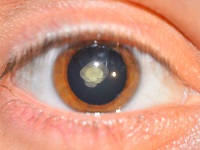
Increased intraocular pressure and associated visual impairment are a symptom of certain diseases, such as strokes.
Its measurement is an important diagnostic aspect in neurological practice, in which partial or complete loss of vision, or a change in its quality, is a precursor of serious pathologies of the nervous system.
Neurological disorders: parkinsonism, stroke
Many celebrities suffered from Parkinson's disease: Pope John Paul II, politician Mao Zedong, artist Salvador Dali, poet A. Voznesensky, actor M. Fox and many others. There is Parkinson's disease and its atypical syndromes due to biochemical changes in the central nervous system (central nervous system). Initially, Parkinson's disease was determined by the presence of characteristic signs.
History reference. The first mention of the disease, very similar to parkinsonism, archaeologists have found in ancient Egyptian manuscripts.
In the second half of the twentieth century, more modern laboratory technologies provided an opportunity to study the pathogenesis of the disease. The name of the disease is in honor of the English scientist J. Parkinson, who wrote in 1817 a detailed work on the subject of “trembling paralysis.” Depending on the progression and severity, various forms and stages of Parkinson's disease are distinguished.

Clinical symptoms of Parkinson's disease: trembling of the extremities, limitation of motor ability, muscle rigidity, postural instability. Labor activity is limited. Atypical form - progressive supranuclear gaze paresis (hereinafter referred to as PSPV), initially differs little from the standard form of Parkinson's disease.
For the disease PSPV characteristic of these types of visual impairment:
- view restriction over 50% (up, down);
- retention of gaze when looking around;
- disorder of eye coordination and head movements. To look away, the person first turns his head, and then performs the corresponding movements with his eyeballs;
- blepharospasm.
From Parkinson's disease, PSPV differs by a slight improvement in the patient's condition for levodopa therapy, rapid progression of the disease.
Other common causes are diseases of the nervous system, which are accompanied by acute cerebral blood flow of varying degrees. In addition to functional pathological changes in the body, stroke is accompanied by organic changes in brain tissue, its structure is disturbed. Occurs due to interruption of blood outflow (it may take only a few minutes).
Ischemia, which lasts more than five minutes, leads to irreversible damage to nerve cells. Sudden blurred vision is often a precursor of apoplexy.
Typical clinical symptoms of the disease:
- face asymmetry;
- paralysis;
- speech disorder;
- convulsive syndrome;
- different forms of amnesia.
Reduction of vision in one eye or both at once, headache, torsion of the face occurs in the first few minutes of an apoplexy stroke.
A stroke causes significant damage to the body, often without the possibility of restoring all its former functions. Cerebral embolism, cerebral thrombosis of the brain - the causes of poor vision, its complete loss.
Long-term rehabilitation is required to restore visual function when vision is reduced due to ischemia. When recurrent seizures or minor microcirculatory disorders observed malfunction of the visual organs of mild.
This is one of the late complications of a dangerous disease - diabetes. It is a lesion in the small blood vessels that feed the retina. Causes of visual impairment: inadequate antidiabetic treatment, toxic effect of glucose (its excessively high level) on the vascular walls. Rapid loss of vision due to retinopathy is observed in patients with advanced forms of severe diabetes, concomitant hypertension, in an elderly patient.
Symptoms of the disease is a visual impairment: "flies flying in front of the eyes," a decrease in sharpness, clarity of vision, double vision, blurred image. The finish of diabetic retinopathy is a complete loss of vision.
What can not be ignored?
People often do not rush to an ophthalmologist with minor violations of visual functions. It happens that the sight has fallen sharply. Some diseases develop without pronounced signs, visual impairment occurs gradually. Therefore, it is important to undergo an annual preventive examination. The earlier they reveal the disease and the causes of visual impairment, the more effectively it is possible to eliminate them, to stop the development of visual ailments. What symptoms should alert?
Vision deteriorates rapidly, in particular, its sharpness decreases. A sharp or gradual progressive decrease in the sharpness of a vision cannot be ignored, especially if its quality of life and work are affected. Pathological change is one-sided (loss of vision in one eye), or vision sits on both eyes in sync.

- Partial or total change in the quality of vision. A person sees objects vague, forked, their forms are not clear.
- Pain in the eyes of varying severity, which is observed at a voltage or at rest, with eyelids drooping.
- Photophobia, feeling of dryness, cutting in eye sockets. They may indicate a variety of infectious lesions, some forms of which are quite dangerous (blenrhea).
If you notice visual impairment in yourself or your loved ones, you should contact an ophthalmologist. The doctor diagnoses any visual defects: he will examine the eyeball, prescribe additional research methods to determine the severity of the changes, the stored functions. What treatment is required - the doctor decides. Progressive vision loss can be stopped with adequate treatment.
Prevention
To avoid problems that are associated with impaired visual function and disrupt activity, and to stop the pathological process, it is recommended to follow the rules of hygiene.
A child needs to be taught from childhood to perform simple gymnastic exercises for the eyes - the unobtrusive play of her form is effective. During work in front of a computer monitor (from radiation is very deteriorated vision), you must take breaks, take the eye exercises. For younger guys, the duration of viewing should not exceed 1.5 hours per day.

A person at risk (for example, a patient with diabetes mellitus), so that his vision does not deteriorate even more, should pay special attention to eye health.
You can not self-medicate the disease, you need to closely monitor the level of sugar in the blood. After all, loss of vision is a strong blow for a person: interest in life disappears, severe depression develops.
The labor activity of the visually impaired and the activity of completely blind people is limited. Today, various social programs are being developed to support and adapt such people in a sighted society.
They allow you to rationally take the free time of the visually impaired.
Visual impairment can occur in childhood as well as in adulthood. Approximately 285 million people in the world have various visual impairments, 45 million of them suffer from total blindness. According to the World Health Organization, about 90% of various types of eye function disorders live in developing countries. The main cause of visual impairment in people around the world are considered unadjusted anomalies of refraction. Cataract is recognized as the dominant disease causing blindness in middle- and low-income countries. According to the findings of scientists, with timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent them and eliminate visual impairment in 80% of cases.
The international classification of diseases provides 4 definitions of the state of vision: normal, moderate visual impairment, severe impairment and blindness. At the same time, moderate and severe disorders can be combined and defined as “reduced vision”.
About 65% of people suffering from vision problems worldwide are people aged 50 years and older, while only about 20% of the population belong to this age group. Visual impairment was found in 19 million children: 1 million 400 thousand of them suffer from complete irreversible blindness.
WHO identified the main causes of visual impairment and the percentage of them among themselves:
43% - unadjusted anomalies of refraction, such as farsightedness, myopia and astigmatism;
33% cataract - partial or complete clouding of the lens, the natural lens of the eye;
2% - glaucoma - damage to the nerve that connects the eye with the brain, caused by hypertension inside the eye.
Despite the progress in the field of surgery and the emergence of new methods of cataract treatment, in many countries of the world (with the exception of the developed ones), it remains the leading cause of visual impairment in 47.9% of cases. Common causes include age-related macular degeneration (AMD), corneal clouding, diabetic retinopathy, congenital blindness, trachoma, and onchocerciasis.
Visual impairment is most often the symptoms of various diseases:
In order to prevent the development of eye diseases recommended:
- undergo regular eye examinations to identify inadequate correction, cataracts, glaucoma and in order to obtain an assessment of the overall health of the eyes
- make eye charges;
- stop smoking because smoking, in addition to all other negative health effects, is associated with the development of cataracts and macular degeneration;
- to treat chronic diseases, in particular diabetes. Careful monitoring of blood sugar levels will help reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, an eye disease. Regular eye examinations for people with diabetes can help detect diabetic retinopathy on early stage development and reduce the risk of complications;
- protect your eyes from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet radiation, such as tanning beds. Wearing UV goggles and a wide-brimmed hat helps limit ultraviolet eye irradiation.
- wear special safety glasses when working with tools (for example, electric welding) and during rest;
- be careful during outdoor activities. Every year there are many eye injuries associated with sports or recreational activities;
- know the family history of the relative vision problems of the relatives, in order to prevent the development of diseases transmitted from generation to generation;
- eat right, paying attention to vitamins and biologically active nutrients that are good for sight.
Foods rich in omega fatty acids, green leafy vegetables contain many valuable nutrients. Vitamins A, C and E are essential for good vision. Lutein and zeaxanthin will help protect the macula (the central part of the retina).
Often the profession and lifestyle are decisive factors in the health of the eyes and the level of vision of a person. For example, drivers often have hyperopia (due to the fact that they look into the distance while driving), and for people working at a computer, on the contrary, myopia, so the monitor is in close proximity. Therefore, it is recommended for drivers to make stops while driving and periodically look in close, for example, at the instrument panel. For people working with small parts and objects, whose vision is rarely directed into the distance, you need to pause for rest and look, for example, at the window, at distant objects. Periodic changes of focus will help to relax the muscles of the eyes and prevent their rapid fatigue.
Although not all eye diseases can be prevented, much can be done to slow their progression and prevent visual impairment. Care for and care of the eyes is crucial for maintaining vision, treating and preventing eye diseases at an early stage, and protecting your overall health. No wonder they say that “the eyes are the mirror of the soul”, because they are capable of speaking as about the psycho-emotional state of a person, and about his health. A number of diseases: diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, HIV and others - are diagnosed according to the symptom of visual impairment.
Take care of your eyes and the priceless gift given to you - sight.
The degree of visual impairment is determined by the ability of the eye to see two glowing points with a minimum distance between them. Normal visual acuity, equal to one - 1.0, corresponds to the ability of a person to distinguish on a special table the tenth row of numbers and letters from a distance of 5 meters. In medicine, there are several in humans.
Classification of violations depending on visual acuity
As a major in medicine, a classification of visual impairment is used depending on the person's ability to see.
- . Inherent complete lack of visual sensations or residual vision. When wearing glasses noted maximum visual acuity - 0.04, or only the ability to light sensation.
- Absolute or total blindness. Characterized by a complete lack of visual sensations or the presence of light sensation, shaped vision with a sharpness of 0.005 to 0.04.
- Visually impaired blindness. Visual acuity from 0.05 to 0.2. With this vision, the eyes perform their informative function.
Classification of visual impairment depending on the time of occurrence of the defect
Depending on the time of occurrence of a defect in ophthalmology, the following classification of visual impairment is distinguished:
- blind born These include all those born with absolute blindness or are blind before the age of 3 years;
- blinded. These are people who have lost the ability to see at the age of more than 3 years.
The basis of this classification of visual impairment is the presence of a partial or completely absent view of the surrounding world.
Visual impairment in various diseases of the visual system
There is a classification of the types of impairment of the visual function depending on the causes of the defect:
- refraction disorder. In this case, the image of the subject is not focused clearly in front of the retina;
- accommodation disorder. This is the inability to clearly see all objects at different distances;
- peripheral vision disorder. There is no clear image of objects in motion or on the sides of the eyes;
- disorder of the adaptive ability of the eye. Impaired vision when changing lighting.
This specification is based on a change in a person’s ability to see, but not in its complete absence.
Each of the listed classifications of impaired ability to see is used by an ophthalmologist to make an accurate diagnosis and is an important criterion for assessing the overall health of a person. Therefore, the degree of visual impairment is determined depending on the severity and cause of the depression of visual sensitivity.
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0